Astronomers around the world are captivated by an unusually bright and long-lasting pulse of high-energy radiation that swept over Earth on Sunday, Oct. 9. The emission came from a gamma-ray burst (GRB)—the most powerful class of explosions in the universe—that ranks among the most luminous events known.
On Sunday morning Eastern time, a wave of X-rays and gamma rays passed through the solar system, triggering detectors aboard NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory, and Wind spacecraft, as well as others. Telescopes around the world turned to the site to study the aftermath, and new observations continue.
Called GRB 221009A, the explosion provided an unexpectedly exciting start to the 10th Fermi Symposium, a gathering of gamma-ray astronomers now underway in Johannesburg, South Africa. “It’s safe to say this meeting really kicked off with a bang—everyone’s talking about this,” said Judy Racusin, a Fermi deputy project scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, who is attending the conference.

The signal, originating from the direction of the constellation Sagitta, had traveled an estimated 1.9 billion years to reach Earth. Astronomers think it represents the birth cry of a new black hole, one that formed in the heart of a massive star collapsing under its own weight. In these circumstances, a nascent black hole drives powerful jets of particles traveling near the speed of light. The jets pierce through the star, emitting X-rays and gamma rays as they stream into space.
Video Player
This sequence constructed from Fermi Large Area Telescope data reveals the sky in gamma rays centered on the location of GRB 221009A. Each frame shows gamma rays with energies greater than 100 million electron volts (MeV), where brighter colors indicate a stronger gamma-ray signal. In total, they represent more than 10 hours of observations. The glow from the midplane of our Milky Way galaxy appears as a wide diagonal band. The image is about 20 degrees across. Credit: NASA/DOE/Fermi LAT Collaboration
The burst also provided a long-awaited inaugural observing opportunity for a link between two experiments on the International Space Station—NASA’s NICER X-ray telescope and a Japanese detector called the Monitor of All-sky X-ray Image (MAXI). Activated in April, the connection is dubbed the Orbiting High-energy Monitor Alert Network (OHMAN). It allows NICER to rapidly turn to outbursts detected by MAXI, actions that previously required intervention by scientists on the ground.
“OHMAN provided an automated alert that enabled NICER to follow up within three hours, as soon as the source became visible to the telescope,” said Zaven Arzoumanian, the NICER science lead at Goddard. “Future opportunities could result in response times of a few minutes.”
The light from this ancient explosion brings with it new insights into stellar collapse, the birth of a black hole, the behavior and interaction of matter near the speed of light, the conditions in a distant galaxy—and much more. Another GRB this bright may not appear for decades.
Video Player
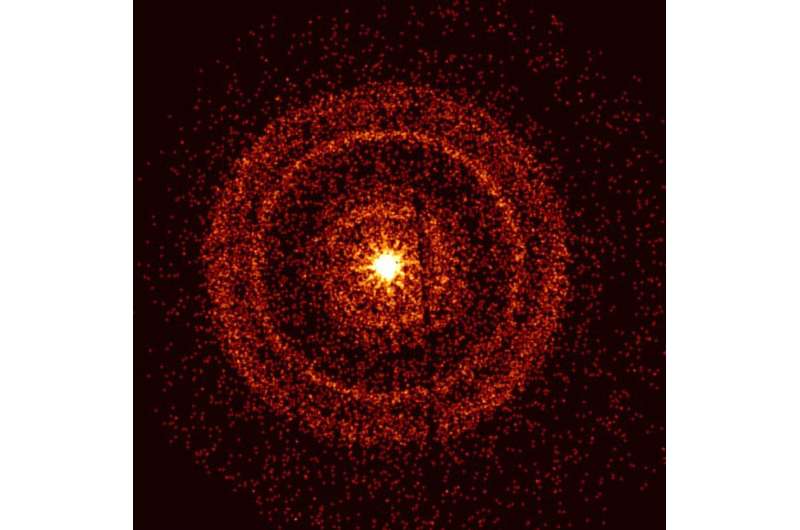
Images taken in visible light by Swift’s Ultraviolet/Optical Telescope show how the afterglow of GRB 221009A (circled) faded over the course of about 10 hours. The explosion appeared in the constellation Sagitta and occurred 1.9 billion years ago. The image is about 4 arcminutes across. Credit: NASA/Swift/B. Cenko
According to a preliminary analysis, Fermi’s Large Area Telescope (LAT) detected the burst for more than 10 hours. One reason for the burst’s brightness and longevity is that for a GRB, it lies relatively close to us.
“This burst is much closer than typical GRBs, which is exciting because it allows us to detect many details that otherwise would be too faint to see,” said Roberta Pillera, a Fermi LAT Collaboration member who led initial communications about the burst and a doctoral student at the Polytechnic University of Bari, Italy. “But it’s also among the most energetic and luminous bursts ever seen regardless of distance, making it doubly exciting.”





